People often assume that the three terms - Product design, UX design and UI design can be used interchangeably. But if that were the case, wouldn’t they all have the same title, right?
Design has come a long way and yet its roles and responsibilities are often misunderstood.
Although the above-mentioned terms are similar to an extent, they still differ by a great margin.
Continue reading the article to find out the similarities and distinctions between them.
PRODUCT DESIGN vs UX DESIGN vs UI DESIGN
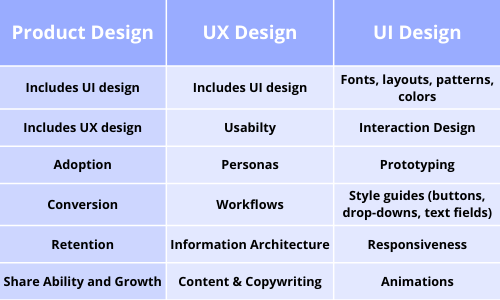
The above displayed table will surely help you gain a better understanding of the three terms and how they are different.
As apparent, UI and UX designs are the subsets of Product design. Along with the UI and UX designs, a product design addresses the business’s unique goals of adoption, retention, conversion and growth.
UI and UX designs are subsets of product design whereas the product design is whole within itself.
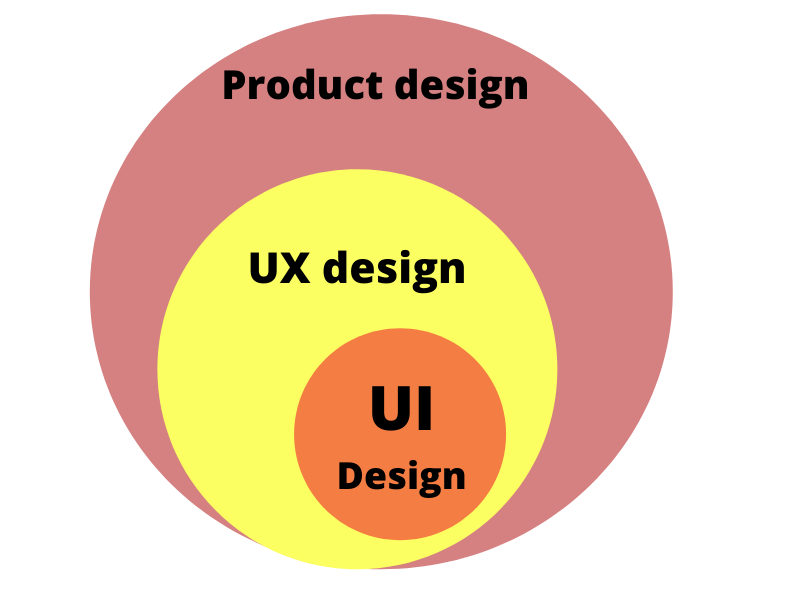
Where UX and UI design falls short, it’s the product design that comes and saves the day.
What Is Product Design?
Product Design is not just about creating something new or improving what already exists; it's a strategic approach that blends art, science, and technology to address the evolving needs of users while pursuing sustainability and innovation.

It's a discipline that sits at the intersection of user desirability, technical feasibility, and business viability. Here's a closer look at its core principles:
- Solves User Problems: Aims to identify and solve real problems faced by users, enhancing the value and utility of the product.
- Integrates Form and Function: Balances aesthetics (form) and usability (function) to create products that are not only beautiful but also highly functional and easy to use.
- Involves Multidisciplinary Collaboration: Brings together experts from various fields, such as design, engineering, and marketing, to ensure the product meets user needs, technical constraints, and market demands.
- Driven by Research: Relies on user research and market analysis to inform design decisions, ensuring the product is tailored to target users' preferences and needs.
- Iterative Development: Utilizes an iterative process, incorporating prototyping, testing, and feedback to refine the product continuously until it meets the desired standards.
- Balances User Needs and Business Goals: Strives to create products that fulfill user needs while achieving business objectives, ensuring the product's market viability and success.
- Sustainability and Ethics: Considers the environmental impact and ethical implications of product design, aiming to create sustainable and socially responsible products.
- Incorporates Technology: Leverages the latest technologies to enhance product functionality and user experience, staying ahead in competitive markets.
What Is UI Design?
UI Design is the meticulous process of creating intuitive, aesthetically pleasing interfaces that facilitate a seamless interaction between the user and the product. It's about transforming complex technology into accessible, navigable, and enjoyable experiences. This discipline combines visual design, interaction design, and usability principles to guide users through a digital landscape. Here are some key points:
- Focuses on Visual Elements: Concentrates on the aesthetics of a product, including layout, typography, color schemes, and icons.
- Enhances Interactivity: Aims to create interfaces that are easy and enjoyable to interact with.
- Crafts Look and Feel: Responsible for the overall look and feel of the product, ensuring it is appealing and engaging for users.
- Visual Hierarchy: Utilizes principles of visual hierarchy to guide users' attention to important elements and functionalities.
- Considers Branding: Integrates branding elements into the design to create a cohesive and recognizable appearance.
- Accessibility: Ensures that the interface is accessible to users of all abilities, incorporating accessible design principles.
What Is UX Design?
UX Design is the art and science of making digital (and physical) products delightful and intuitive to use. It’s about understanding the human behind the screen—their desires, challenges, and behaviors—and crafting experiences that not only solve problems but also bring joy and ease into their daily interactions with technology. By focusing on the user's journey through a product, UX Design seeks to create a seamless, efficient, and memorable experience. Here are some key points:
- Enhances User Satisfaction: Focuses on increasing the joy and satisfaction users experience when interacting with a product.
- Improves Usability & Accessibility: Aims to make products more usable and accessible to users, ensuring that everyone can efficiently use them.
- Based on User Needs: Involves thorough research on users' needs, behaviors, and motivations to design solutions that meet their objectives seamlessly.
- Creates Seamless Experiences: Strives to design intuitive user experiences that allow users to achieve their goals with minimal effort or confusion.
- Iterative Process: Involves continuous testing and refinement based on user feedback to improve the design progressively.
PRODUCT DESIGN vs UX DESIGN
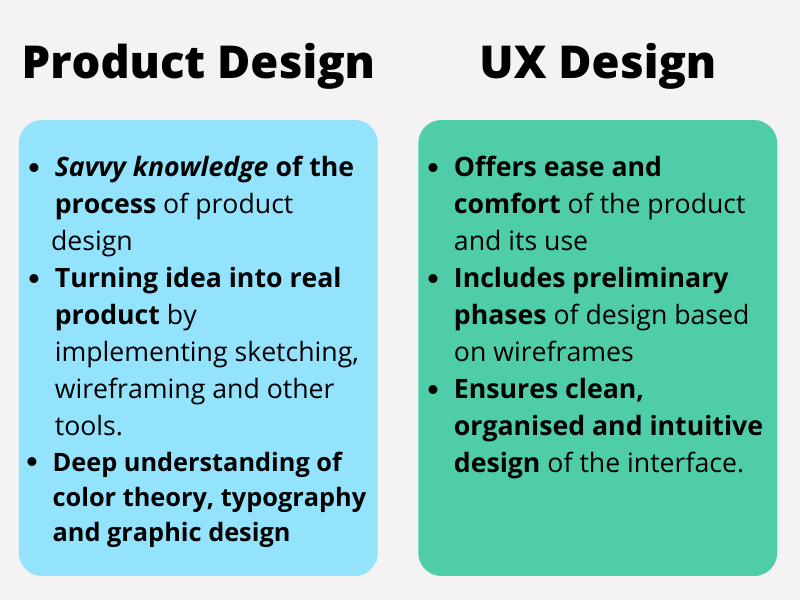
The very first clear distinction between product design and UX design is- UX designer spends his time developing products prior to the launch, whereas on the other hand, product designers spend their time in updating products that have already been launched.
A product designer focuses on the business needs whereas the UX designer is concerned with user requirements.
Here is an illustration of some other key differences between the two-
PRODUCT DESIGN vs UI DESIGN
On one hand where a UI designer focuses on the color, font, patterns or typography of the product, the product designer handles the whole process from start to finish.
A UI designer enhances the cosmetic changes and looks of the product, whereas a product designer performs the function of both UI designer and a UX designer.
UX DESIGN vs UI DESIGN
A UX design focuses on anything that can affect the user's journey to solve a problem both on screen and off. On the other hand, UI design focuses on how the product looks and appeals.
One simple example for this is, If you go to a restaurant, consider the UI as a table, chair, glass, plates and furniture. And the UX is everything right from the food to the ambience, service and parking. If you want to know more about the difference between UX and UI, click here.
Frequently Asked Questions on Product Design Vs. UX Design Vs. UI Design
Ques 2: What tools do Product, UX, and UI Designers use?
Ans: While it's possible for one person to have skills in all three areas, each discipline requires specialized knowledge and skills. Some professionals are skilled in multiple areas, especially in smaller companies or startups. However, larger companies often prefer specialists who can contribute deep expertise in their respective areas.
Ques2: What tools do Product, UX, and UI Designers use?
Ans: Common tools include Sketch, Adobe XD, and Figma for UI and UX design; for Product Design, tools like Jira for project management, and various prototyping tools are used. The choice of tools can depend on the specific needs of the project and the team's preferences.
Ques 3: How important is a collaboration between Product, UX, and UI Designers?
Ans: Collaboration is crucial. Although each role has its own set of responsibilities, a successful product requires seamless integration of all three disciplines. Regular communication and feedback sessions can help ensure that the product meets user needs and business goals.
Ques 4: How do Product Design, UX Design, and UI Design impact the success of a product?
The combined efforts of Product, UX, and UI Design are essential for creating a product that meets user needs, achieves business objectives, and stands out in the market. Good design can lead to increased user satisfaction, higher engagement rates, and ultimately, commercial success.


